Pedigrees practice human genetic disorders – Pedigrees, powerful tools in the realm of genetics, provide a systematic approach to tracing the inheritance patterns of human genetic disorders. By analyzing these visual representations of family health histories, researchers and clinicians gain invaluable insights into the causes, modes of transmission, and potential risks associated with these complex conditions.
Delving into the intricacies of genetic disorders, we explore their diverse types, common examples, and underlying mechanisms. Pedigrees emerge as essential tools for deciphering the genetic basis of these disorders, enabling us to comprehend their inheritance patterns and predict their likelihood of occurrence within families.
Genetic Disorders
Genetic disorders are conditions caused by alterations in the DNA sequence of an individual. These alterations can range from small changes in a single nucleotide to large-scale chromosomal rearrangements.
Types of Human Genetic Disorders
- Single-gene disordersare caused by mutations in a single gene. These disorders can be inherited in an autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked pattern.
- Chromosomal disordersare caused by changes in the structure or number of chromosomes. These disorders can be inherited or acquired.
- Multifactorial disordersare caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. These disorders include common conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Examples of Common Genetic Disorders
- Cystic fibrosisis an autosomal recessive disorder that affects the lungs, pancreas, and other organs.
- Sickle cell anemiais an autosomal recessive disorder that affects the red blood cells.
- Down syndromeis a chromosomal disorder caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21.
Causes of Genetic Disorders
Genetic disorders can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Mutationsare changes in the DNA sequence that can occur spontaneously or be inherited from parents.
- Chromosomal rearrangementsare changes in the structure or number of chromosomes that can occur during cell division.
- Environmental factorscan also play a role in the development of genetic disorders. For example, exposure to certain chemicals or radiation can increase the risk of developing cancer.
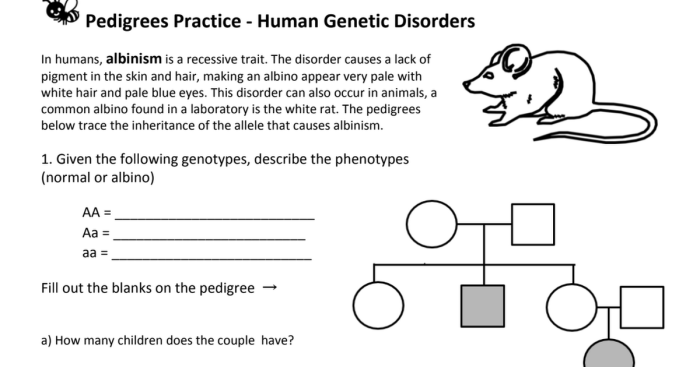
Pedigrees: Pedigrees Practice Human Genetic Disorders
Pedigrees are diagrams that represent the inheritance of genetic traits within a family. They are used to track the transmission of genetic disorders and to identify individuals who may be at risk for developing a disorder.
Purpose of Pedigrees
- To identify the mode of inheritance of a genetic disorder.
- To predict the likelihood of future family members inheriting a disorder.
- To identify individuals who may be at risk for developing a disorder.
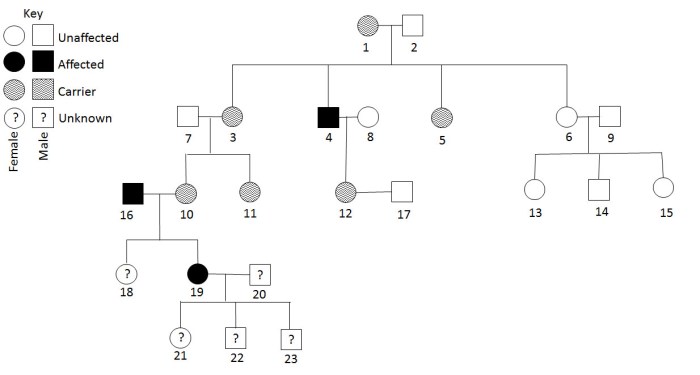
Creating and Interpreting Pedigrees, Pedigrees practice human genetic disorders
Pedigrees are created using standard symbols to represent individuals and their relationships. The following are some of the most common symbols used in pedigrees:
- Squaresrepresent males.
- Circlesrepresent females.
- Linesconnecting individuals represent relationships.
- Shaded symbolsrepresent individuals who have a genetic disorder.
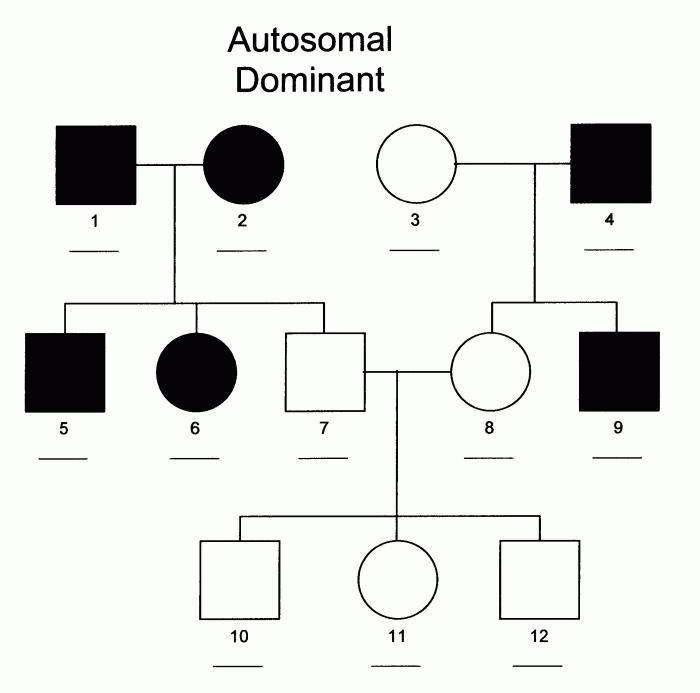
Pedigrees can be used to determine the mode of inheritance of a genetic disorder. The mode of inheritance refers to the pattern of transmission of a disorder from parents to offspring. The three main modes of inheritance are:
- Autosomal dominant
- Autosomal recessive
- X-linked
Practice Using Pedigrees
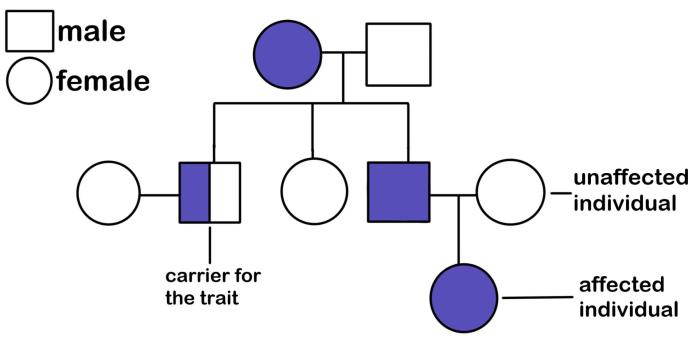
The following is an example of a pedigree for a hypothetical family with a genetic disorder:

The pedigree shows a family with a history of cystic fibrosis. The proband (the individual with the disorder) is indicated by the arrow. The proband’s parents are unaffected, but they are both carriers of the cystic fibrosis gene. The proband’s siblings are also unaffected, but they have a 25% chance of being carriers of the cystic fibrosis gene.
The pedigree can be used to determine the mode of inheritance of cystic fibrosis. In this case, the disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. This means that both parents must be carriers of the cystic fibrosis gene in order for their child to develop the disorder.
The pedigree can also be used to predict the likelihood of future family members inheriting cystic fibrosis. The proband’s siblings have a 25% chance of being carriers of the cystic fibrosis gene. If they have children, their children will have a 1 in 4 chance of inheriting the disorder.
Ethical Considerations
The use of pedigrees raises a number of ethical considerations. These considerations include:
- Informed consent: Individuals should be informed about the purpose of the pedigree and their right to refuse to participate.
- Privacy: Pedigrees contain sensitive information about individuals’ health. This information should be kept confidential.
- Respect: Pedigrees should be used respectfully and responsibly. Individuals should not be stigmatized or discriminated against based on their genetic information.
The following are some guidelines for using pedigrees respectfully and responsibly:
- Obtain informed consent from all individuals included in the pedigree.
- Keep pedigree information confidential.
- Use pedigrees for legitimate purposes only.
- Respect the privacy and dignity of individuals included in the pedigree.
FAQ Explained
What are the ethical considerations associated with using pedigrees?
Pedigree analysis involves collecting sensitive genetic information, necessitating informed consent from all participants. Confidentiality and privacy must be strictly maintained to protect individuals’ rights and prevent potential stigmatization.
How can pedigrees help predict the likelihood of inheriting a genetic disorder?
By analyzing inheritance patterns within pedigrees, geneticists can estimate the probability of an individual carrying a specific genetic variant or developing a particular disorder. This information aids in genetic counseling and decision-making.