Hesi case study peptic ulcer disease – HESI Case Study: Peptic Ulcer Disease: An In-Depth Exploration of Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Peptic ulcer disease, a prevalent gastrointestinal ailment, demands meticulous examination. HESI case studies offer an invaluable platform to unravel the complexities of this condition, empowering healthcare professionals with a comprehensive understanding of its pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management strategies.
Introduction: Hesi Case Study Peptic Ulcer Disease
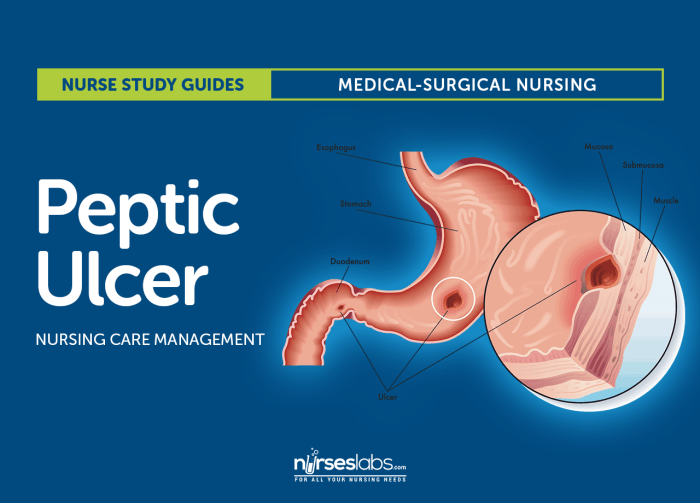
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a common condition that affects the lining of the stomach and small intestine. It is estimated to affect approximately 10% of the global population. HESI case studies provide a valuable tool for understanding the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of PUD.
Pathophysiology of Peptic Ulcer Disease
PUD develops when the protective mechanisms of the gastric mucosa are compromised, allowing acid and pepsin to damage the underlying tissue. Contributing factors include:
- Helicobacter pyloriinfection
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use
- Increased gastric acid secretion
- Impaired mucosal defense mechanisms
Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Peptic Ulcer Disease
Common symptoms of PUD include:
- Abdominal pain
- Heartburn
- Dyspepsia
- Nausea and vomiting
Diagnosis is confirmed through endoscopic examination, such as upper endoscopy or capsule endoscopy. Biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions, such as gastric cancer.
Treatment Options for Peptic Ulcer Disease, Hesi case study peptic ulcer disease
Treatment options for PUD aim to reduce acid secretion, promote healing, and prevent complications. Medications include:
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
- Histamine-2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs)
- Antacids
Endoscopic therapies, such as endoscopic mucosal resection and argon plasma coagulation, may be used for larger ulcers. Surgery is rarely necessary.
Nursing Management of Peptic Ulcer Disease
Nurses play a crucial role in providing care to patients with PUD. Nursing interventions include:
- Patient education
- Medication administration
- Symptom management
- Monitoring for complications
Case Study Analysis
A 55-year-old male presents with a history of epigastric pain, heartburn, and dyspepsia. Endoscopy reveals a gastric ulcer. The patient is diagnosed with PUD and prescribed a PPI. Nursing interventions include:
- Educating the patient on PUD and its management
- Administering the PPI as prescribed
- Monitoring the patient for adverse effects of the medication
- Encouraging the patient to follow a healthy diet and lifestyle
Key Questions Answered
What is the primary cause of peptic ulcer disease?
Infection with Helicobacter pylori bacteria is the most common cause of peptic ulcer disease.
What are the typical symptoms of peptic ulcer disease?
Common symptoms include abdominal pain, heartburn, and indigestion.
How is peptic ulcer disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis is typically confirmed through endoscopy and biopsy.
What are the treatment options for peptic ulcer disease?
Treatment options include medications, endoscopic therapies, and surgery.
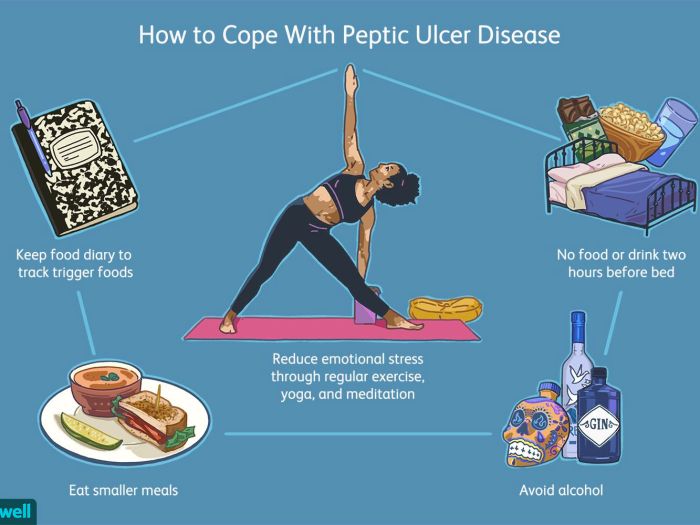
What is the role of lifestyle modifications in managing peptic ulcer disease?
Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding smoking and alcohol consumption, can help reduce symptoms and promote healing.