Select the correct proper or common name for the compound – Navigating the intricate world of chemical nomenclature, this article explores the significance of selecting the correct proper or common name for a compound. Understanding the rules and conventions governing compound naming is paramount, ensuring clear communication, safety, and accurate scientific research.
Delving into the criteria for determining proper names, we uncover the use of prefixes, suffixes, and root words in constructing compound names. A comprehensive table or list will provide a valuable reference, correlating common names with their corresponding proper counterparts.
Nomenclature and Conventions
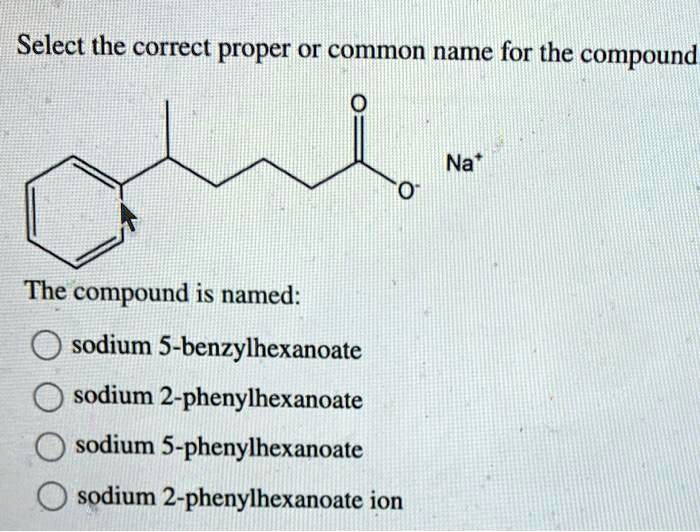
Correct nomenclature is crucial in chemical compounds to ensure clear communication and avoid confusion. It involves following established rules and conventions to name inorganic and organic compounds systematically.
Inorganic compounds are named based on their constituent elements, using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element. For example, NaCl is sodium chloride, while Fe2O3 is iron(III) oxide.
Organic compounds are named based on their structure, using prefixes to indicate the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain and suffixes to indicate the functional groups present. For example, CH3CH2OH is ethanol, while C6H12O6 is glucose.
Identifying Proper and Common Names
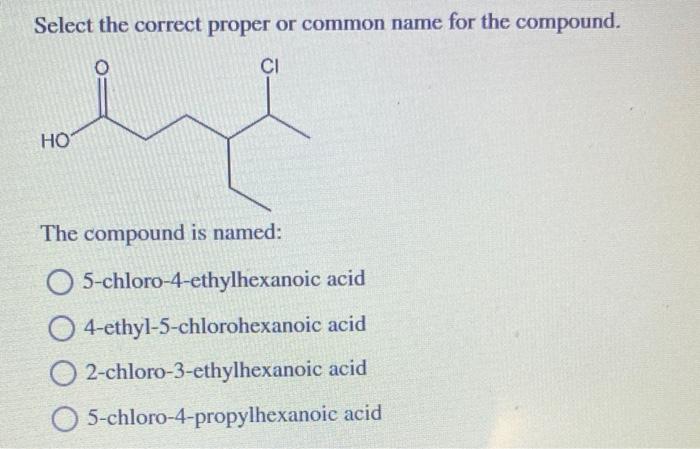
The proper name of a compound is its systematic name, which follows the established rules and conventions. Common names, on the other hand, are often used for convenience and may vary depending on the context.
To determine the proper name of a compound, it is important to identify its structure and functional groups. Prefixes and suffixes are then used to construct the systematic name according to the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) guidelines.
| Common Name | Proper Name |
|---|---|
| Baking soda | Sodium bicarbonate |
| Table salt | Sodium chloride |
| Rubbing alcohol | Isopropyl alcohol |
Structural Analysis
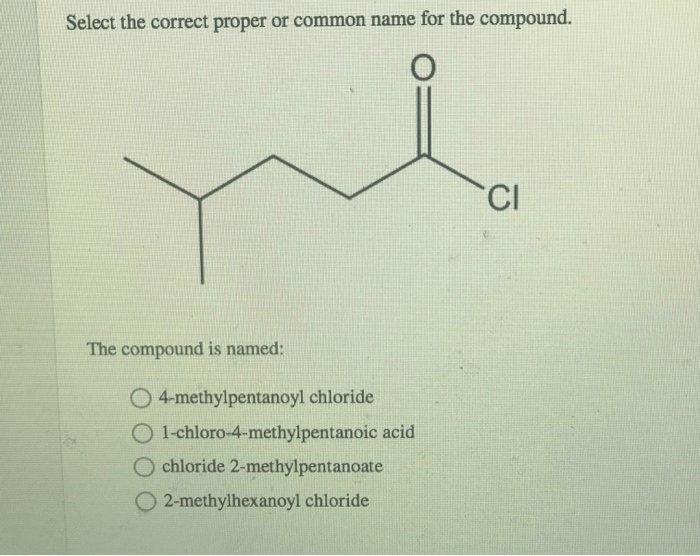
The structure of a compound can be deduced from its name. Functional groups are indicated by specific suffixes, while prefixes indicate the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain.
For example, the name “butanoic acid” indicates that the compound has a four-carbon parent chain and a carboxylic acid functional group. The name “2-propanol” indicates that the compound has a three-carbon parent chain and a hydroxyl group attached to the second carbon atom.
Applications and Implications: Select The Correct Proper Or Common Name For The Compound
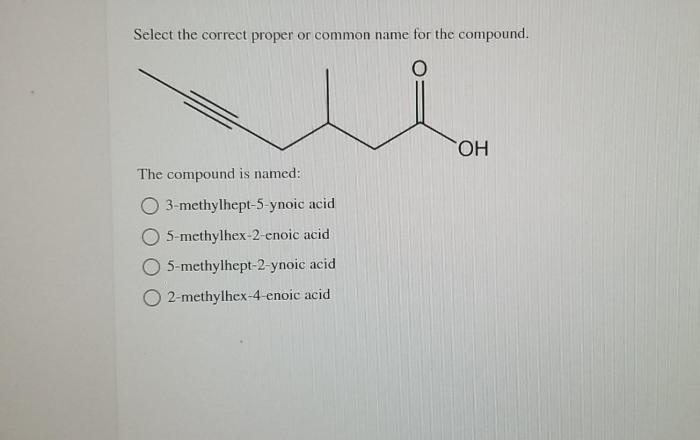
Correct compound naming is essential in various fields, including chemistry, medicine, and engineering.
- Safety:Accurate naming ensures that compounds are handled and stored safely, as incorrect naming can lead to confusion and potential hazards.
- Communication:Systematic naming allows chemists to communicate about compounds clearly and unambiguously, facilitating research and collaboration.
- Research:Correct naming helps researchers identify and retrieve information about compounds, enabling efficient literature searches and the development of new knowledge.
Quick FAQs
What are the key criteria for determining the proper name of a compound?
The proper name of a compound is typically based on its structure, considering the presence of functional groups, prefixes, and suffixes that indicate specific molecular features.
How can I differentiate between a proper name and a common name for a compound?
Proper names follow systematic rules and conventions, while common names are often derived from historical or descriptive origins and may vary depending on the context.