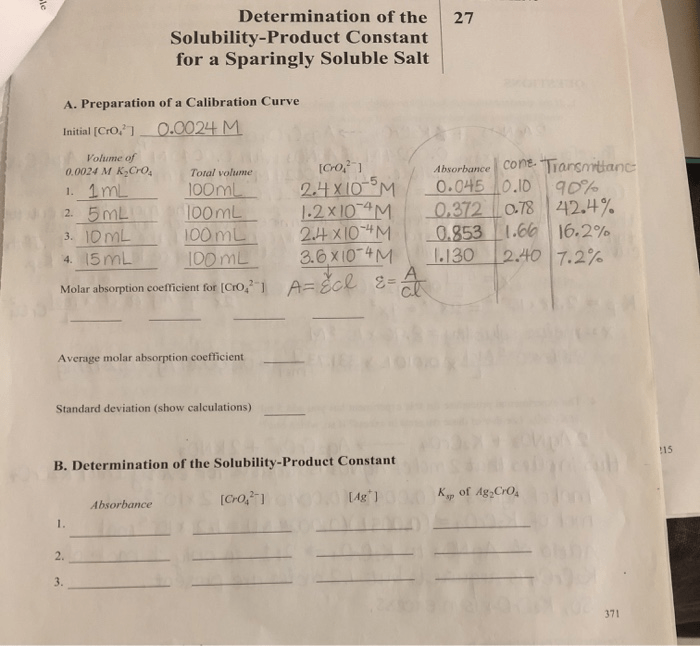
Determination of the solubility-product constant for a sparingly soluble salt – Determination of the solubility-product constant (Ksp) for sparingly soluble salts is a fundamental concept in chemistry, providing valuable insights into the behavior of these compounds in aqueous solutions. Understanding Ksp is crucial for comprehending the solubility of sparingly soluble salts, which have limited solubility in water.
This guide delves into the experimental methods used to determine Ksp, including gravimetric, conductometric, and spectrophotometric analyses. It explains the steps involved in calculating Ksp from experimental data and discusses the use of graphs and tables to analyze the results.
Furthermore, the guide explores the factors that can affect Ksp, such as temperature, ionic strength, and pH.
Determination of the Solubility-Product Constant for a Sparingly Soluble Salt
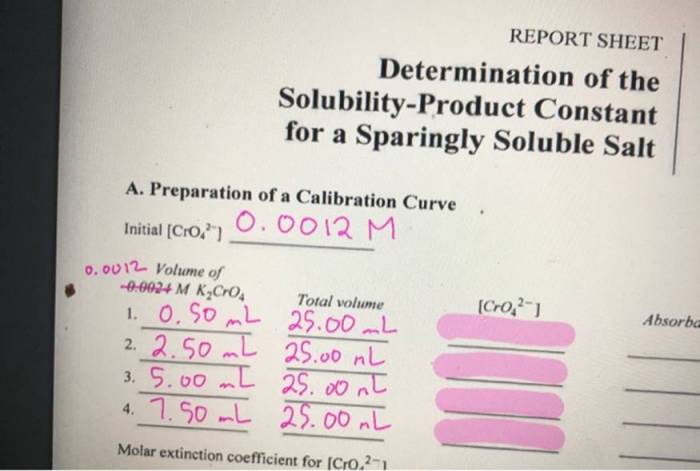
The solubility-product constant (K sp) is an equilibrium constant that describes the solubility of a sparingly soluble salt in a solvent. It is defined as the product of the molar concentrations of the ions of the salt in a saturated solution.
K spis an important parameter in understanding the solubility of sparingly soluble salts. It can be used to predict the solubility of a salt in a given solvent, and to calculate the concentration of the ions of the salt in a saturated solution.
Experimental Methods
There are several methods that can be used to determine the K spof a sparingly soluble salt. These methods include:
- Gravimetric analysis
- Conductometric analysis
- Spectrophotometric analysis
Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of method will depend on the specific salt being studied and the available equipment.
Data Analysis, Determination of the solubility-product constant for a sparingly soluble salt
Once the experimental data has been collected, it can be used to calculate the K sp. The following steps are typically involved in the data analysis:
- Calculate the molar solubility of the salt.
- Calculate the molar concentrations of the ions of the salt in the saturated solution.
- Calculate the Kspusing the following equation:
Ksp= [cation] n[anion] m
where [cation] and [anion] are the molar concentrations of the cation and anion of the salt, respectively, and n and m are the stoichiometric coefficients of the cation and anion in the balanced chemical equation for the dissolution of the salt.
Factors Affecting Ksp
The K spof a sparingly soluble salt can be affected by several factors, including:
- Temperature
- Ionic strength
- pH
The temperature dependence of K spis typically small. However, the ionic strength and pH of the solution can have a significant effect on K sp.
Applications of Ksp
K sphas a number of practical applications in various fields, including:
- Analytical chemistry
- Environmental chemistry
- Pharmaceutical chemistry
In analytical chemistry, K spis used to determine the solubility of sparingly soluble salts and to calculate the concentration of ions in a solution.
FAQ Resource
What is the significance of Ksp?
Ksp is a quantitative measure of the solubility of sparingly soluble salts, indicating the extent to which they dissolve in water.
How can Ksp be used in analytical chemistry?
Ksp is used in analytical chemistry to determine the concentration of sparingly soluble salts in solution through techniques such as gravimetric analysis.
What factors influence the Ksp of a sparingly soluble salt?
Temperature, ionic strength, and pH are the primary factors that can affect the Ksp of a sparingly soluble salt.