Congress in a flash answers icivics – Congress in a Flash Answers: An Unparalleled Guide to the Legislative Branch takes readers on an enlightening journey through the intricacies of the American political system. This comprehensive resource delves into the fundamental role of Congress, its structure, leadership, and representation, providing a clear understanding of how laws are made and how the government operates.
Through a captivating narrative and meticulous research, Congress in a Flash Answers unravels the complexities of congressional oversight, ethics, and the challenges faced by the legislative branch. It offers a unique perspective on the inner workings of Congress, empowering readers with a deeper understanding of the American political landscape.
Congress in the U.S. Government
Congress is the legislative branch of the U.S. government, responsible for making laws and overseeing the executive branch. It is a bicameral body, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives.
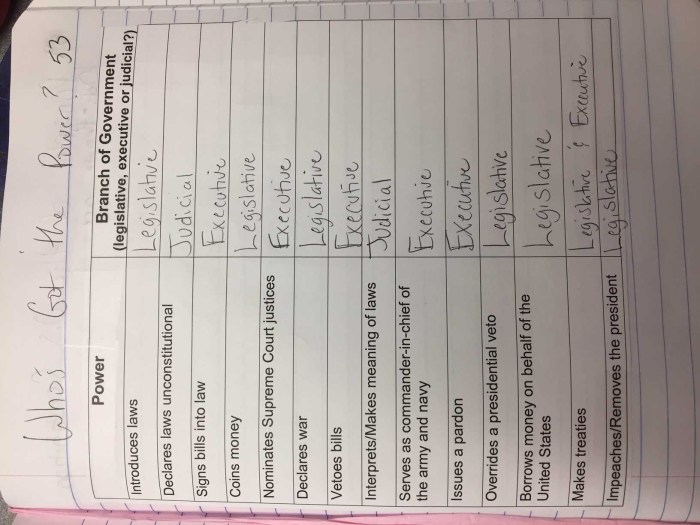
Powers and Responsibilities of Congress
- Making laws
- Declaring war
- Approving treaties
- Raising revenue
- Impeaching the President
- Overseeing the executive branch
Congress has exercised its authority in numerous ways throughout history, such as passing the Declaration of Independence, the Constitution, and the Civil Rights Act.
The Structure of Congress: Congress In A Flash Answers Icivics
The Two Chambers of Congress
- Senate:100 members, two from each state, elected for six-year terms.
- House of Representatives:435 members, elected for two-year terms, apportioned among the states based on population.
The Process of How a Bill Becomes a Law
- A bill is introduced in either the Senate or the House.
- The bill is referred to a committee for consideration.
- The committee may hold hearings and make amendments to the bill.
- The bill is reported out of committee and placed on the floor for debate.
- The bill is voted on by the full chamber.
- If the bill passes, it is sent to the other chamber for consideration.
- The other chamber may make amendments to the bill.
- The bill is voted on by the full chamber.
- If the bill passes both chambers, it is sent to the President for signature.
- The President may sign the bill into law or veto it.
- If the President vetoes the bill, it can be overridden by a two-thirds vote of both chambers.
The Role of Committees in the Legislative Process
Committees play a vital role in the legislative process by reviewing bills, holding hearings, and making recommendations to the full chamber. There are various types of committees, including standing committees, select committees, and conference committees.
Congressional Leadership

Key Leaders in Congress
- Speaker of the House:Presides over the House of Representatives and is second in line to the presidency.
- President of the Senate:Presides over the Senate and is the Vice President of the United States.
- Majority Leader:The leader of the majority party in each chamber, responsible for scheduling legislation and managing the floor.
- Minority Leader:The leader of the minority party in each chamber, responsible for providing an alternative perspective and holding the majority party accountable.
Organization and Management of Congress
Congress is organized into various caucuses, committees, and subcommittees. These groups allow members to specialize in specific policy areas and work together to advance their agendas.
Influence of Congressional Leadership
Congressional leaders play a significant role in shaping the legislative agenda and influencing the outcome of bills. They control the flow of legislation, set priorities, and negotiate compromises.
Congressional Representation
Election of Members of Congress
- Senators are elected by the voters of their state.
- Representatives are elected by the voters of their congressional district.
- Congressional districts are drawn by state legislatures, which can lead to gerrymandering.
Gerrymandering and Its Impact on Representation
Gerrymandering is the practice of drawing congressional districts to give one political party an unfair advantage over another. This can result in distorted representation and make it difficult for minority groups to elect candidates of their choice.
Diversity of Congress and Its Implications for Policymaking
The diversity of Congress has increased in recent years, with more women, minorities, and LGBTQ+ members serving. This diversity brings a wider range of perspectives and experiences to the legislative process, which can influence policymaking.
Congressional Oversight

Role of Congress in Overseeing the Executive Branch, Congress in a flash answers icivics
Congress has the power to oversee the executive branch, ensuring that it is acting in accordance with the law and the Constitution.
Tools for Conducting Oversight
- Hearings
- Investigations
- Subpoenas
- Impeachment
Examples of Congressional Oversight
Congress has used its oversight authority to investigate a wide range of issues, including the Iran-Contra affair, the Watergate scandal, and the Benghazi attack.
Congressional Ethics
Ethical Standards for Members of Congress
Members of Congress are subject to a number of ethical standards, including conflict of interest rules, gift bans, and disclosure requirements.
Process for Enforcing Ethical Rules
The House Ethics Committee and the Senate Ethics Committee are responsible for investigating and enforcing ethical rules for members of their respective chambers.
Challenges in Maintaining Ethical Standards
Congress faces a number of challenges in maintaining ethical standards, including the influence of money in politics, the pressure to raise funds, and the partisan nature of the political environment.
Quick FAQs
What is the primary function of Congress?
Congress serves as the legislative branch of the American government, responsible for making laws and overseeing the executive branch.
How many chambers are there in Congress?
Congress consists of two chambers: the Senate and the House of Representatives.
What is the process for passing a bill into law?
A bill must pass both the House and Senate before it can be sent to the President for signature. If the President signs the bill, it becomes law.
What role do committees play in the legislative process?
Committees review and debate proposed legislation before sending it to the full chamber for a vote.
What is the purpose of congressional oversight?
Congressional oversight involves monitoring the actions of the executive branch to ensure that it is operating within the bounds of the law.